FGT think your best choice in the future
System Integration Designers in FGT
- 2022-05-03
- 5:01 pm
An article to understand the principles of various flowmeters, and the dynamic diagram is clear!
Principles and applications of various flowmeters
In piping design, due to the negligence and lack of experience of designers, unreasonable pipeline layout, inconvenient operation and maintenance, and unsightly appearance are often caused. In order to improve the design quality and reduce the occurrence of common sense errors, we have summarized the most commonFlowmeterExamples!
According to the fluid characteristics, piping material, piping pressure, piping temperature, piping flow direction, etc. are all taken into consideration, then we start to choose which type of flowmeter is more suitable for us to use in piping design: and do a good jobStatistics of fluid-related parameters such as: pipeline temperature, pipeline pressure, fluid viscosity, fluid velocity, fluid flow, fluid pH, fluid conductivity, fluid
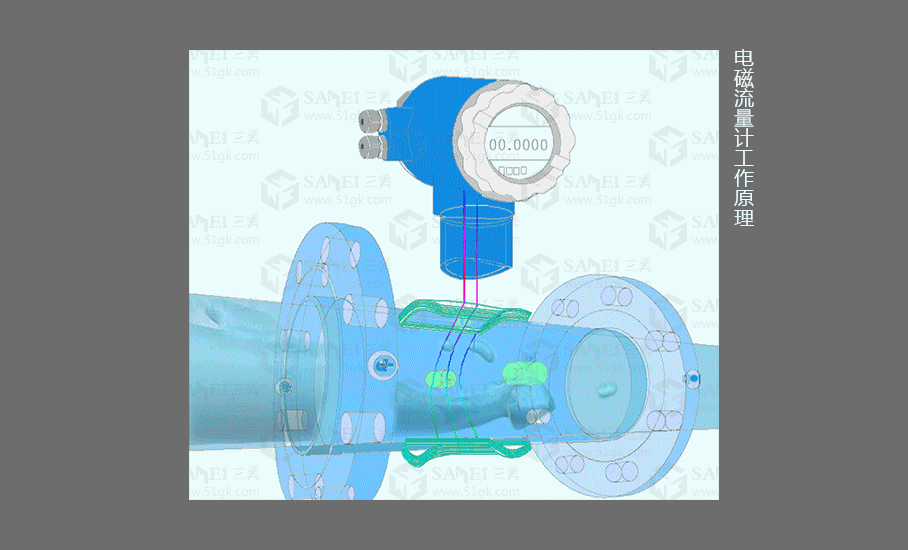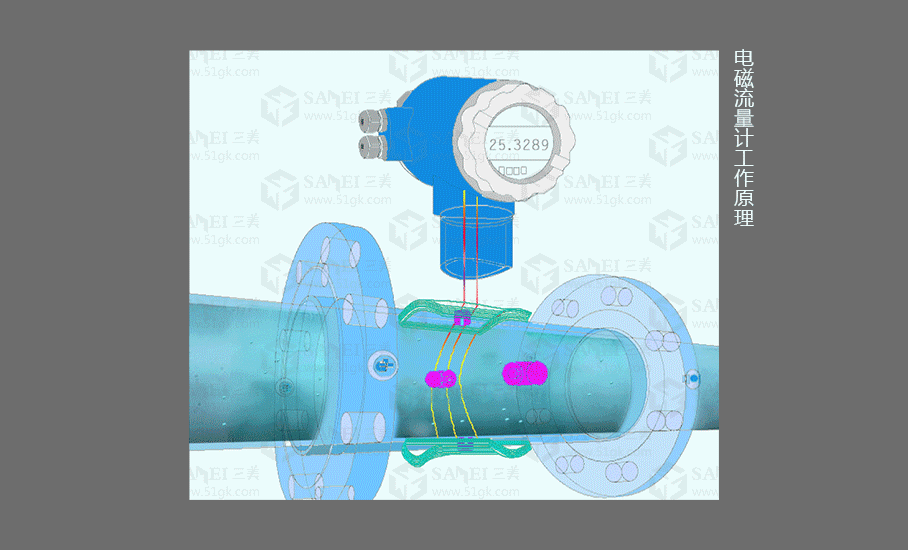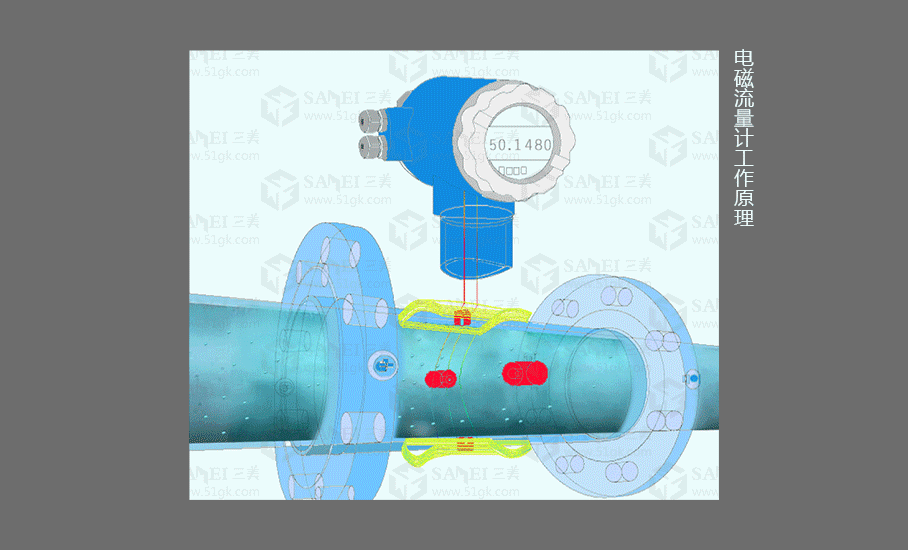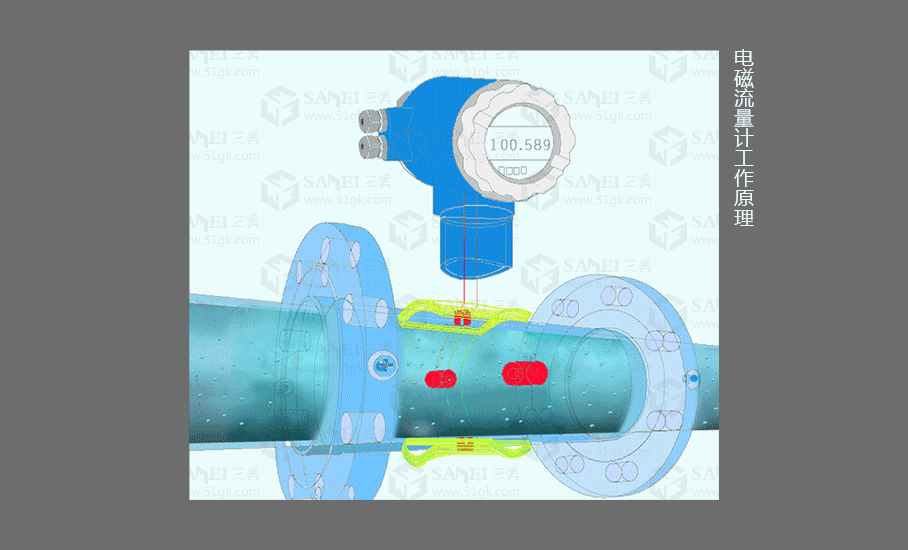
1.Electromagnetic Flowmeter
Applicable fluid
Various acids, gallium, salt solution, raw water, cooling water, sewage, coal slurry FMG electromagnetic flowmeter, ore slurry, mud, cement slurry, paper pulp, syrup, coal water slurry, corn steep liquor, fiber slurry, grain slurry, lime milk, hydrogen peroxide , volume flow of fluids and solid-liquid two-phases with conductivity characteristics such as beer, wort, black liquor, green liquor and various beverages
working principle
The (integrated) FMG electromagnetic flowmeter consists of a sensor and a converter. It is based on Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and is used to measure the volume flow of conductive liquids with a conductivity greater than 5μS/cm. It is an inductive instrument for measuring the volume flow of conductive media. In addition to measuring the volume flow of general conductive liquids, it can also be used to measure the volume flow of strong corrosive liquids such as strong acid and alkali, and uniform liquid-solid two-phase suspension liquids such as mud, ore pulp, and paper pulp.
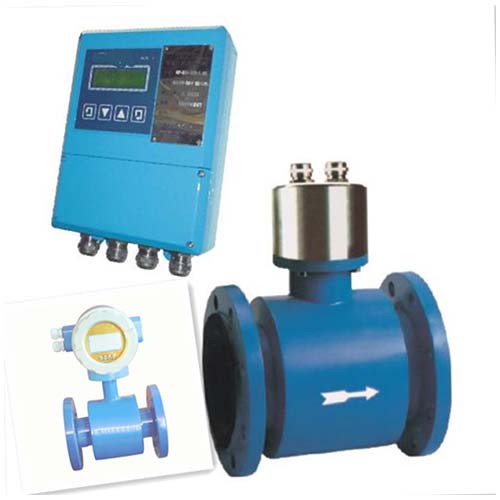

lackpoint
1.fluid without conductivityFor example, pure water, petroleum products and organic solvents cannot use FMG electromagnetic flowmeter2.
2.Mounting Orientation Restrictions: Special lining protection is required for vertical installation, no such restriction for horizontal installation
3.On-site environmental restrictions: The installation environment requires good power supply quality, and the grounding measures need to be grounded
2. Ultrasonic flowmeter
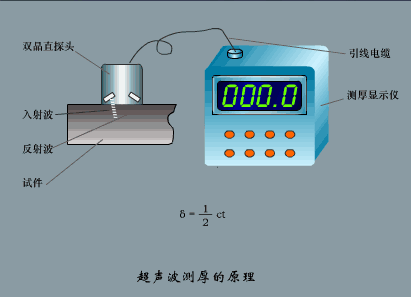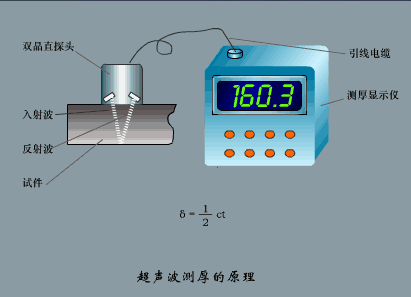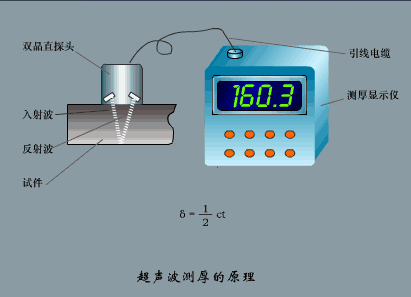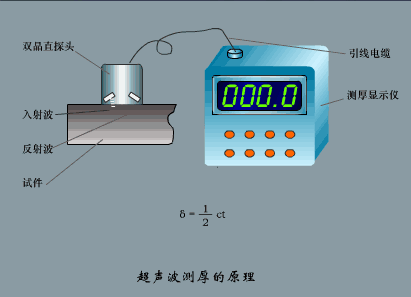
Applicable fluid
UFM ultrasonic flowmeter is a non-contact flowmeter, which can measure the flow of medium with large diameter and can be used for the measurement of medium that is not easy to touch and observe. It has high measurement accuracy and is hardly disturbed by various parameters of the measured medium, especially to solve the flow measurement problems of strong corrosive, non-conductive, radioactive and flammable and explosive media that other flow meters cannot.
working principle
The UFM ultrasonic flowmeter adopts the time difference measurement principle: after a probe transmits a signal through the pipe wall, the medium, and the other side of the pipe wall, it is received by another probe. At the same time, the second probe also transmits a signal and is transmitted by the first probe. It is received that there is a time difference Δt between the two due to the influence of the medium flow rate. According to the calculation, the conversion relationship between the flow rate V and the time difference Δt can be obtained. V=(C2/2L)×Δt, and then the flow value Q can be obtained.
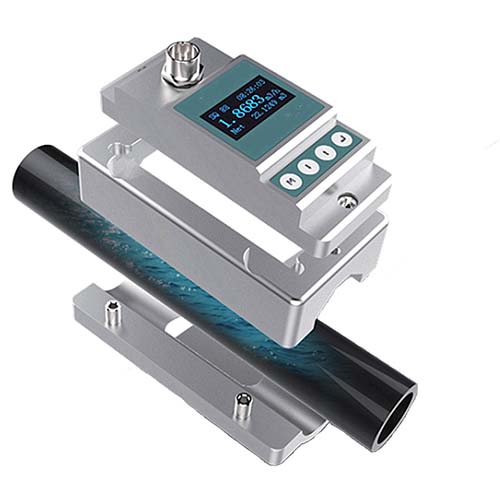

shortcoming
1.Traffic restrictions:It cannot be used in fluids whose pipeline flow rate is less than 1/2 of the pipe diameter, and the flow rate of the medium is measured in the range of 1.0-12.0m/s
2.Tube Restrictions:Can not be used on pipes with galvanized material
3.Fluid Limits:Can not be used in liquids mixed with oils and fluids with bubble characteristics
4.Temperature Limits:Can only be used to measure fluids below 200°C
3. Rotameter/area flowmeter/floating value flowmeter
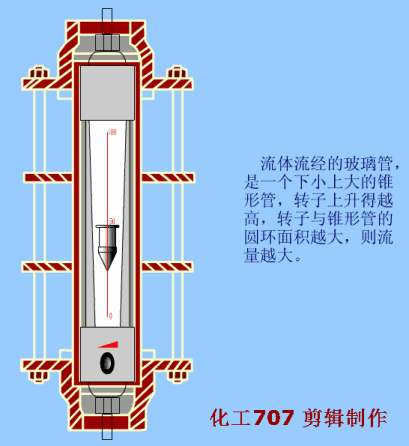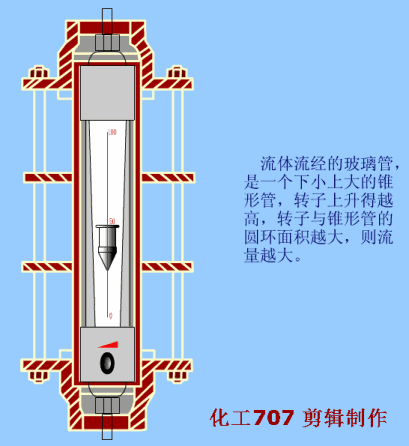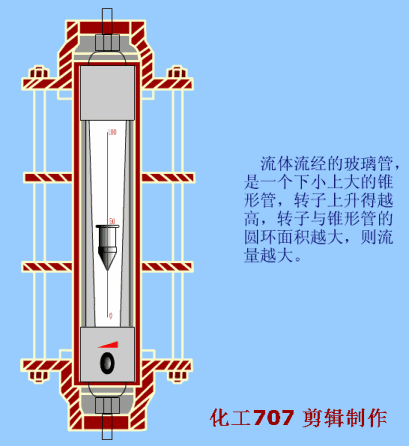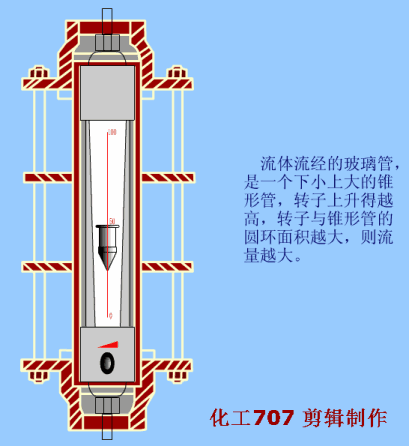
Applicable fluid
PFM glass rotor/float/area flowmeter: It has strong corrosion resistance, can detect the flow of acid (except hydrofluoric acid), fluoride, oxidant and other corrosive gases or liquids, suitable for chemical, pharmaceutical, paper, sewage treatment and other industries
PFB plastic rotor/float/area flowmeter: Simple structure, intuitive, small pressure loss, easy maintenance and so on. Rotameter is suitable for measuring small flow through pipeline diameter D<150mm
working principle
Float flowmeter, also known as rotameter, is a device that estimates the flow by measuring the (position) of the rotating parts in the DC pipeline. It is a type of variable area flowmeter. In a vertical conical tube that expands from bottom to top, the gravity of the circular cross-section float is supported by hydrodynamic forces, and the float can rise and fall freely within the conical tube. It moves up and down under the action of flow rate and buoyancy, and after balancing with the weight of the float, it is transmitted to the dial to indicate the flow through magnetic coupling. The metal tube rotameter is mainly composed of three parts
a, indicator (intelligent indicator, local indicator)
b. float
c. Conical measuring chamber
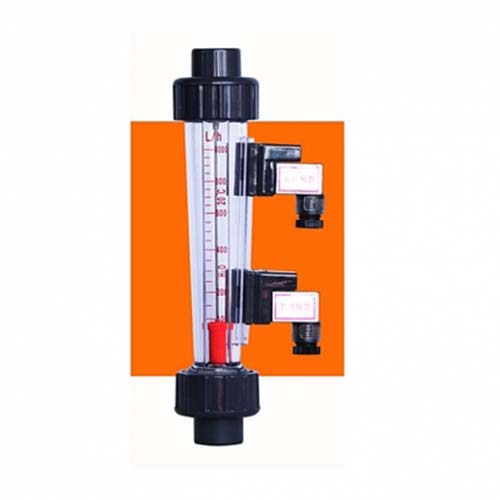

shortcoming
1. Viewing angle: Due to the viewing angle of the eye and the installation position, the displayed value is different when the viewing angle is above or below.
2. Glass tube characteristics: The glass tube is suitable for corrosive fluids, but it is easy to be damaged during installation, and it is not easy to install
3. No data: because of the use of mechanical characteristics and no cumulative flow data can be calculated