FGT think your best choice in the future
System Integration Designers in FGT

Smart Building Automation

System integration design
IoT custom design

Smart Manufacturing Automation
FGT MEP Engineering System Designer | Flow Meter Manufacturing
FGT®【First General Technology Co., Ltd.】System Integration Manufacturer of MEP Electromechanical Engineering
(Flowmeter, SCADA/HMI system, multi-channel temperature controller) manufacturing production company
[Professional MEP Engineering System Integration | Flow Meter Manufacturer]
Professional manufacturer to produce water flow meter, gas flow meter, engineering design of AI artificial intelligence smart building system, central monitoring system design, intelligent temperature controller, IoT and APP software production design manufacturer
Building Weak Current Business Group
Weak current engineering|Operation content
conform to
Smart Building Label Grade Design in Taiwan: Silver, Gold, Diamond
International LEED level design: American green buildingCertificationLEED 40 – 49 points: passcertified 50 – 59 points: Silvercertified · 60 – 79 points: Goldcertified · Above 80 points: Platinum levelcertified
FTTH fiber to the home: designed by MDF/OLDF in line with NCC submission standards
Improved design for mobile communication signal boosters in basements and elevators
Including bullet cameras, dome cameras and other IP POE digital surveillance systems, DRV and NVR digital video recorders, IVS electronic fence
Dual system design of license plate recognition and Etag parallel operation, lane management and parking fee management design
Embedded System (EmbeddedSystem) Touch Phone Recording Answering Machine USB Recording Box
Air-blown optical fiber construction, micro-cluster optical fiber construction
Design and Construction of DTV Digital Channel and BS Satellite Antenna
The building's full-network video intercom system includes design, planning and construction of large door phones, small door phones, and indoor door phones
IP Broadcast Module. MD-1. Ceiling Speaker. Wall Mount Speaker. IP Broadcast Module. MD-1. IP Broadcast Module. MD-1. Speaker. Gooseneck. Microphone. Broadcast area.Switcher.Music playback.Time list
Due to its short wavelength, UHF has strong penetrability and is suitable for indoor fields with many obstacles, such as engineering construction, factory monitoring, security patrol, restaurants, KTV, restaurants, hotels and other indoor or floors In many occasions; in addition, the frequency of use of business-type license-free radio walkie-talkies is also within the scope of UHF
Weak current integration systemInterface description. 1. Smart box in the house in Area Asystem. BooksystemWith the smart box module equipment in the house, the interface description is as follows:. (1) networkmodule. This device is composed of common antennalight electricityProvided by the manufacturer, Light Generation Data Switch .
Complete enterprise-level IP-PBX product: IP-PBX is the core of enterprise VoIP system, it can expand the characteristics and functions of enterprise voice phone, covering complete data, voice, and video services, such as Unified Messaging and other features. It also includes the following special features:
‧ Auto Provision
‧ Personalized multi-language automatic switchboard function (Auto Attendant)
‧ Multi-person audio conference (Meet-Me)
‧ Instant call recording (Recording)
It also provides other advanced functions such as: three-tier automatic switchboard voice response system (IVR), voice conference room, call park, and notification of unread voice messages by email or sending unread voice files as attachments Advanced features that traditional switches cannot provide, such as voice message system and web-based management interface. IPBX-1825 also provides expandable FXO or FXS interface, which is a very stable embedded system. All system settings, voice messages and call records can be stored in other external storage devices. Administrators can back up system configuration files to their own computers through the web management interface. In case the system is damaged, the administrator only needs to restore the system backup.
Electricity, central air-conditioning, lighting, sanitary water supply and drainage, air supply and exhaust, elevators, and fire protection systems of smart buildings can all be included in the central monitoring system, which at least has the functions of equipment usage status and fault monitoring, event handling and historical records
Professionally designed transnational multilingual App enables residents with multilingual languages to have a design that takes care of the positions of residents, management committees, property companies, and surrounding stores.
Comprehensively grasp the internal energy of buildings such as water, electricity, gas, heat, etc., integrate statistical analysis data, and provide energy consumption indicators/abnormal diagnosis/energy early warning. Combined with power distribution, water supply, air-conditioning and other systems, the quantitative management xAI model is connected to realize energy forecasting and consumption reduction applications, helping enterprises make good use of resources.
Production business group
Flow Meter|Control Panel|Operation Content
- Electromagnetic Flowmeter
- Turbine flowmeter
- Coriolis flowmeter
- Karman Vortex Flowmeter
- Mass flowmeter
- mass flow controller
- Steam Flow Meter (Vortex Flow Meter/Turbine Flow Meter)
- Symbol value flowmeter
- Diaphragm pneumatic valve
- Gas Panel/Valve Distribution Box (VMB/P)
- Automatic gas cylinder cabinet
- PLC/DDC control panel
- Central monitoring panel
- 41U Telecom Data Cabinet
- MDF telecom distribution frame/OLDF optical fiberpatch panel
- DI/DO module
- AI/AO module
- RS485 module
- NB-IoT module
- AIoT module
Industrial Central Monitoring Business Group
Integration of mechanical and electrical central monitoring system | Operation content
- WebAccess <Advantech>
- Indusoft <ICPDAS Technology>
- IFIX <Funtech Technology>
- Intouch <Conexant Technologies>
- FMCS400 <Whole Plant Monitoring>
- Customization of communication protocol conversion for various instruments and equipment
- MODBUS RTU/TCP conversion service
- OPC Client Newsletter Writing Service
- Graphical control software components, development and writing of plug-in components
- Software and hardware communication interface driver programming
- Controller (PLC, PAC, DDC) firmware writing
- Web-based monitoring graphical interface writing
- Database Software Authoring Services
- Graphic control customization or auxiliary report software writing
- Cloud Database Compose
- SIEMENS S7-400
- FATEK PLC
- AB Logix1400
- ORMON CJ2M
- ABB AC500
- Graphic Control System Auxiliary Components
- MODBUS 485 Auxiliary Components
- 4G/5G wireless and NB-IoT auxiliary components
- Auxiliary components for access control systems
- Visual C# (general program editing software)
- BCB C++ (general program editing software)
- HTML5 (Mobile App Editing)
- MySQL/ MS SQL / Oracle (database language)
- python (written by artificial intelligence deep learning)
News

Recommend a vendor specializing in low-voltage electrical design and NCC design drawing production.
The following are recommended companies in Taiwan that can handle "low-voltage design + NCC design drawing production (including review documents and system planning)" related needs (including low-voltage design/system integration and engineering planning services):

News Summary 2026-02: International Smart Building Abstract
The following is a summary of important news in the field of smart buildings (international) in February 2026, covering market trends, industry dynamics, technologies and events 📊🏙️:
List of Taiwanese low-voltage electrical design companies, what type of company is the first general-purpose one?
Taiwan's low-voltage electrical design field includes many professional engineering service providers. For your specific needs...
Our performance area
TOP 500 brand group companies choose to cooperate with FGT Group
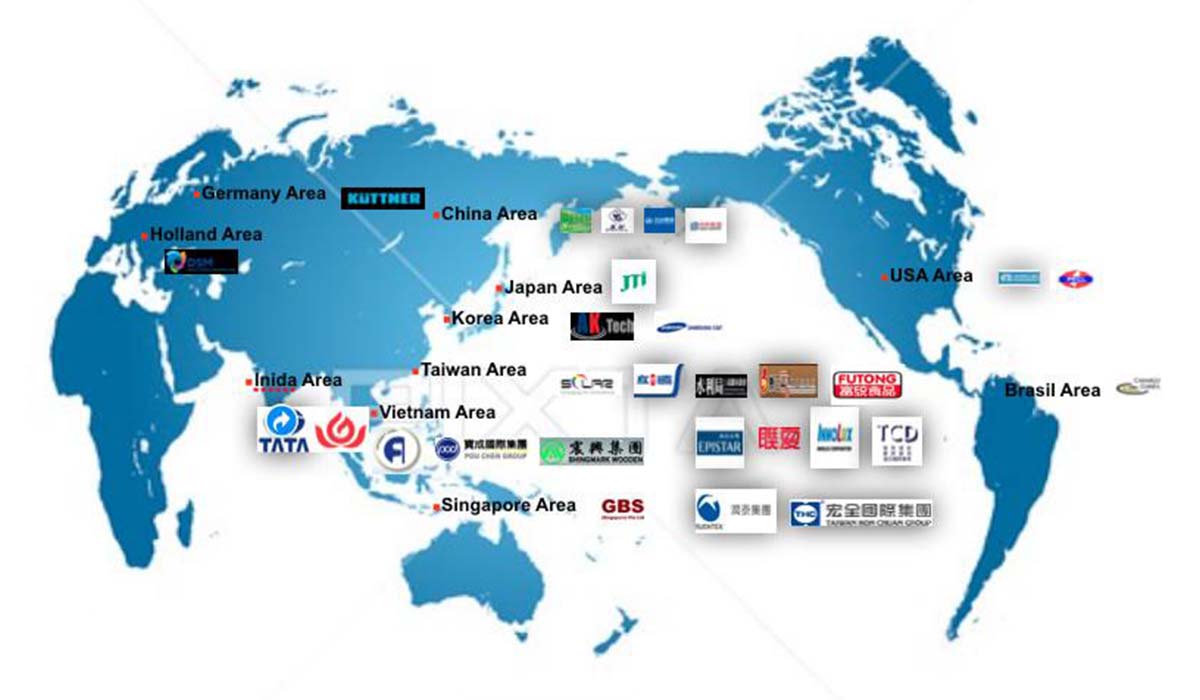

Extensive service portfolio
FGT provides customers with comprehensive one-stop engineering design and consulting services. In addition, FGT manages all engineering work and expertise required for the project in a very competent manner.
Provide gas flowmeters, water flowmeters, wastewater flowmeters, steam flowmeters, electromagnetic flowmeters, vortex flowmeters, mass flowmeters, area flowmeters
Supply pneumatic valve, electric valve, check valve, angle valve
Supply PID temperature controller, multi-point temperature controller
Supply pressure switch, differential pressure sensor, diaphragm pressure gauge, vacuum pressure gauge
System integration design
> IoT APP development and design> AI solution> Cloud system
Flow Meters and OEM/ODM Solutions
> Gas Flow Meters> Water Flow Meters
Smart Manufacturing Automation
> FMCS400 central monitoring system> TY08/15 multi-temperature panel> PLC programming> SCADA graphic control design> gas distribution panel> control panel
Our performance
We bring together the right people to challenge established mindsets and drive transformational outcomes