FGT think your best choice in the future
System Integration Designers in FGT
Introduction to Smart Healthcare and Architectural Medicine
Smart healthcare and architectural medicine are two important contemporary concepts that together can promote the sustainability and efficiency of health care facilities.
Smart healthcare uses advanced technologies, such as big data, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, etc., to improve the efficiency and quality of medical services.
Architectural medicine is an emerging interdisciplinary field that combines architecture and medicine to enhance human health and well-being by improving architectural design and the built environment.
Smart medicine and architectural medicine are two important contemporary concepts
Smart healthcare and architectural medicine are two important contemporary concepts that together can promote the sustainability and efficiency of health care facilities.
- Smart Healthcare:
- Smart healthcare uses advanced technologies, such as big data, artificial intelligence, Internet of Things, etc., to improve the efficiency and quality of medical services.
- In medical facilities, smart medical care can be applied to medical record management, diagnostic support, medical image analysis, remote monitoring, etc., helping to improve the personalization and accuracy of medical services.
- Through smart technology, hospitals can better manage medical resources, reduce waste, and improve the overall patient experience and satisfaction.
- Building Medicine is an emerging interdisciplinary field that combines architecture and medicine to enhance human health and well-being by improving architectural design and the built environment. This field focuses on how the built environment affects the physical and mental health of its occupants, and how to design and build healthy, comfortable living and working spaces. Here are some of the main aspects of architectural medicine:
- Indoor air quality: Study how to improve indoor air quality and reduce pollutants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), dust mites and mold to reduce the risk of respiratory illnesses.
- Natural light and lighting design: Emphasize the importance of natural light and study how to optimize lighting design to enhance people's mood and productivity, and improve sleep quality.
- Acoustic Environment: Explore how to control noise and improve the acoustic environment to reduce the negative health effects of noise pollution, such as stress and sleep disruption.
- Temperature and Humidity Control: Study of how to maintain appropriate temperature and humidity levels to provide a comfortable indoor environment and avoid conditions of overcooling or overheating, thus reducing associated health problems.
- Bioadaptive Design: Using natural materials and design elements, such as greenery and water features, to create an environment that is in harmony with nature, helping to reduce stress and enhance physical and mental health.
- Accessible design: Ensuring buildings are accessible and friendly to all, including older people and people with disabilities, thereby promoting good health and social inclusion.
- Ergonomics: Optimizing the design of furniture and equipment to support correct posture and reduce musculoskeletal problems.
The goal of architectural medicine is to create healthy built environments through scientific research and design practice to improve the overall health and quality of life of its occupants.
Smart Buildings in Architectural Medicine
Smart Buildings refer to buildings that use advanced technologies and systems to improve the operational efficiency, safety, energy saving and user comfort of the building through automation, intelligence and Internet technology. Smart buildings integrate a variety of technologies to enable smarter, more sustainable building management and operations.
The following are the main features and applications of smart buildings:
- Automation system:
- The automation system can control the building's lighting, air conditioning, water supply, drainage and other facilities, and adjust energy use according to different times and usage needs, thereby saving energy and reducing emissions.
- Smart energy management:
- Use sensors, monitoring systems and predictive analytics to optimize energy use and improve energy efficiency, such as adjusting lighting and air conditioning systems to reduce energy consumption.
- Building security and surveillance:
- Integrate security facilities such as video surveillance, intrusion detection, and fire alarm systems to achieve comprehensive monitoring and immediate response capabilities inside and outside the building.
- Smart space management:
- Use wireless sensing technology and smart devices to manage space usage and improve the efficiency and convenience of public areas such as offices and conference rooms.
- Improved user experience and comfort:
- Provide intelligent environmental control, adjust the indoor environment, such as temperature, light, etc., according to the user's preferences and needs, to improve the user's comfort and work efficiency.
- Data analysis and decision support:
- Collect and analyze building operation data through big data analysis, provide decision support, and optimize facility management and resource allocation.
- Sustainability and environmental protection:
- Promote the efficient use of resources and reduce waste, and achieve environmentally friendly and sustainable development of buildings through renewable energy, green materials and water-saving technologies.
Smart buildings are not only innovations in construction technology, but also an important practice that combines technology with environmental sustainability. It can not only improve the operational efficiency and energy saving level of the building, but also improve the quality of life and work of users, in line with today's society's pursuit of smart, convenient and sustainable lifestyles.
What are the integrations of smart medical care and smart buildings?
Smart Clinic
The outpatient calling system refers to the system used by hospitals or clinics to manage outpatient queuing and calling. Such systems usually include the following elements:
- Number calling machine: Usually a display screen or audio system used to display or play the number or name of the current patient who should be seen.
- queue number system: Each patient will receive a unique queuing number or serial number when registering at a clinic or hospital, and the system manages the calling order based on these numbers.
- Call management software: A software system used to manage and control the calling process. It is usually integrated with the queuing number system and supports various output methods for displaying calling information.
- Calling robot or system: Some modern systems may also include voice or text message notification functions to remind patients to go to the corresponding consultation window or clinic.
- Backend management system: A backend management interface used to set up and manage the calling process. You can adjust the distribution rules of queuing numbers and set the display content of different medical departments.
The purpose of the outpatient calling system is to improve the efficiency of patient treatment, reduce patient waiting time, and manage the allocation of hospital resources. Modern dialing systems can often also be integrated with electronic medical record systems and appointment systems to further optimize the overall process and quality of medical services.
- prowill
- bicom
- ECC
Smart nurse call system
Nurse Call System is a common communication system in medical institutions, aiming to provide effective communication and services between patients and caregivers. These systems are often designed to allow patients to easily call nurses or other medical personnel and respond promptly to their needs or emergencies.
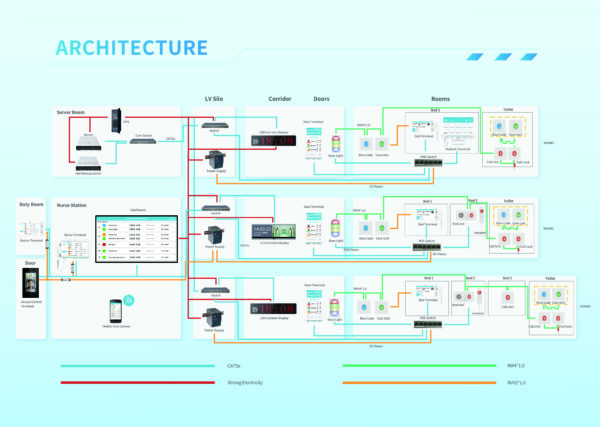
Here are some of the key features and functionality of a nurse call system:
- Buttons and call devices:
- Patients can typically signal a call by pressing a button, pulling on a cord, or using a wireless remote control. These devices are usually installed near the hospital bed or in the ward, allowing patients to signal for help when needed.
- nurse station receiver:
- The call signal is instantly transmitted to the nurse station or designated nursing workstation. The nurse or caregiver can immediately know which patient needs help and respond quickly.
- Sound and light prompts:
- Nurse call systems usually use alert sounds, lights, or displays to alert nurses or other staff that there are emergency calls that need to be handled.
- Internal communication function:
- Some advanced nurse call systems can also provide internal communication capabilities, allowing nurses to communicate directly with each other and ensuring that emergencies are handled quickly.
- Location recognition function:
- The system may display patient location information when a nurse receives a call, allowing the nurse to quickly locate the patient who needs assistance.
- Recording and monitoring:
- The system can record call time, response time and processing results, helping medical institutions analyze and improve service efficiency.
- Integrate other systems:
- Modern nurse call systems can usually be integrated with the hospital's electronic medical record system, nursing management system, etc. to further improve collaboration efficiency and service quality.
The setting up and operation of the nurse call system can significantly improve the quality of patient care, enable nursing staff to respond quickly to patients' needs, and also improve the hospital's operational efficiency and employee satisfaction.
Common Taiwanese IP nurse call system brands
- aristel
- Anpao
- ECC
Smart next-generation medical information HIS system
Health Information System (HIS) refers to a system used to manage and process medical and health-related information. It is an essential part of organizations such as hospitals, clinics, and healthcare institutions, and is designed to effectively manage medical data, improve the quality of medical services, enhance decision support, and promote medical information sharing.
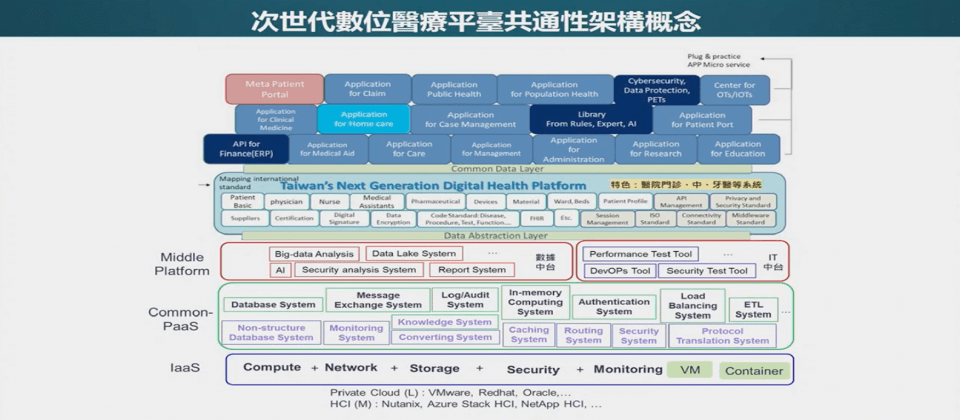
The following are the main functions and components of a medical information system:
- Electronic Health Record (EHR):
- Electronic medical records are the core components of HIS and are used to record and manage patients' health information, medical records, diagnoses, treatment plans, examination results, etc. It replaces traditional paper medical records and provides a more convenient and accurate information management method.
- Electronic Medical Record (EMR):
- EMR is mainly used for the daily clinical operations of doctors and medical teams, including patients' detailed medical history, prescriptions, medical orders, etc. It is usually part of the HIS and is closely related to the electronic medical record.
- Hospital Management Information System (HMIS):
- HMIS covers the management functions of hospitals and medical facilities, including appointment management, bed management, financial management, material management, human resources management, etc., helping to improve hospital operational efficiency and resource utilization.
- Medical Image Management System (Picture Archiving and Communication System, PACS):
- PACS is used to store, retrieve, transmit and display medical images, such as X-ray, CT, MRI, etc. It is integrated with other HIS components to facilitate doctors to review and analyze image data.
- Real-time Location System (RTLS):
- RTLS is used to track moving equipment, medical personnel, and patients in medical facilities to improve safety and efficiency within the facility.
- Decision Support System (DSS):
- DSS uses data analysis and algorithms to provide clinical decision support, helping doctors and medical professionals make more accurate diagnosis and treatment decisions.
- Health Information Exchange (HIE):
- HIE allows different medical institutions to securely share and access patient health information, promoting the integrity of patient medical history and smooth collaboration.
- Mobile Health Applications:
- With the advancement of mobile technology, many HIS have developed mobile applications to allow doctors and patients to access and manage health information anytime and anywhere.
The goal of medical information systems is to improve the quality and efficiency of medical services, reduce errors and duplication of work, and support the comprehensiveness and continuity of clinical decision-making and patient management. These systems are not only critical to the operation of healthcare organizations, but also have a profound impact on patient outcomes and health outcomes.
Common HIS brands in Taiwan
- Outlook
- Yaosheng
- Xingxiang
Architectural Medicine and BIM MEP Design
The BIM MEP model refers to the mechanical, electrical engineering and piping (MEP) model in Building Information Modeling (BIM). BIM is an integrated design and construction process that enables the creation and management of the physical and functional features of a building project on a digital platform. MEP is the abbreviation of Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing engineering, which is a key engineering part of the construction project.
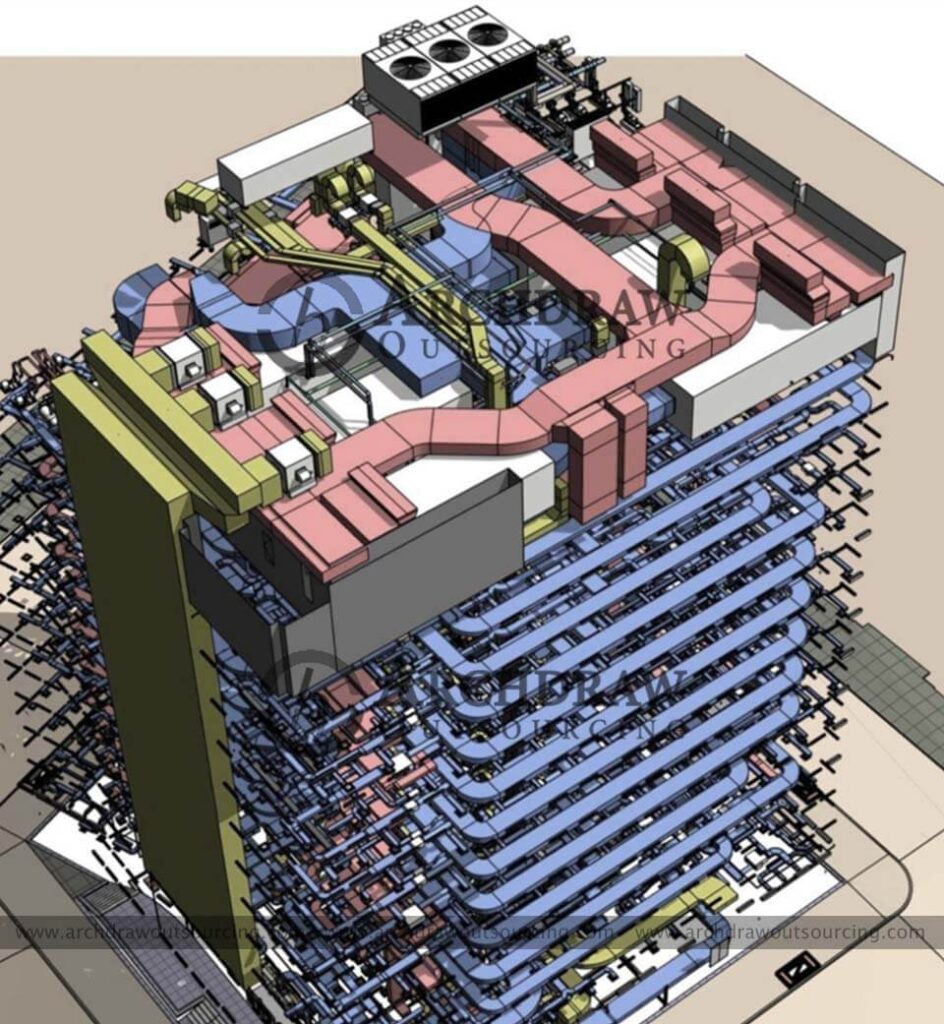
The main features and applications of BIM MEP models include:
- Integrated design and collaboration:
- BIM MEP models can integrate electromechanical piping system design, modeling mechanical, electrical, and piping equipment together with building structures and other construction engineering elements. This integrated design promotes collaboration and communication between engineers from different disciplines, reducing design conflicts and errors.
- Certainty and accuracy:
- Through accurate three-dimensional simulation, the BIM MEP model can more accurately predict and simulate the operating effects and interactions of electromechanical systems, such as the cooling effect of air conditioning systems, load distribution of power systems, etc.
- Visualize and review:
- 3D models allow engineering teams and owners to visually view and review the design of electromechanical systems, including equipment layouts, piping routes, cable channels, etc., which helps identify and resolve potential design issues in advance.
- Design optimization and cost control:
- The BIM MEP model can help engineers and designers optimize the design by simulating different design solutions, performing performance comparisons and cost estimates, thereby achieving the purpose of saving energy and resources.
- Construction and operation and maintenance management:
- BIM MEP models not only help with optimization during the design phase, but also provide support during the construction and operation and maintenance phases. The detailed information contained in the model can be used for construction progress control, material procurement and subsequent maintenance management.
In summary, BIM MEP models not only improve the design efficiency and accuracy of electromechanical piping systems, but also increase the effectiveness and sustainability of the entire construction project. Its application in the construction industry is becoming more and more popular and it is one of the important technical tools in the modern design and construction process.
Architectural Medical Planning Vendors
Below we make an overview and evaluation table for the capabilities of manufacturers that want to become architectural medicine.
| planning ability | Smart medical | architectural medicine | next generation medical | Design talent ability | Manufacturer |
| Medical major | must | must | must | Medical management talents are available | FGT cooperates with hospitals |
| information and communications technology | must | must | Prepared ICT/PLC/IOT talents | FGT own technology | |
| hospital information system | must | must | Familiarity with SQL databases | FGT cooperates with HIS manufacturers | |
| Cloud technology | must | Cloud information security management talents | FGT own technology | ||
| architectural design | must | must | Architectural talents | FGT collaborates with architects | |
| BIM 3D MEP | must | must | REVIT CAD Talent | FGT own technology | |
| digital twin technology | must | must | U&nity development talents | FGT own technology |
Which system planner in Taiwan has the qualifications to engage in next-generation medical care?
The ECC smart weak current design team under FGT is an early independent design team for smart buildings.
The team members’ execution ability is evaluated as follows:
| ECC design team | Experience and execution ability |
| Medical major | Participated in the Vietnam Revitalization Hospital Construction Project |
| information and communications technology | The team has more than 15 years of experience in PLC, IOT and other categories. |
| hospital information system | Familiar with SQL serial connection technology and familiar with SCADA system construction |
| Cloud technology | Existing development results assist in the cloudization of smart buildings |
| architectural design | Equipped with weak current design of building drawings and smart label submission planning |
| BIM MEP | Participate in public works and social housing implementation projects |
| digital twin technology | Independently publishes the application of ECC300 Digital Twin to the campus central warfare system |